Basics for Image Processing¶
What is a kernel?¶
A kernel is essentially a fixed size array of numerical coefficeints along with an anchor point in that array, which is tipically located at the center.
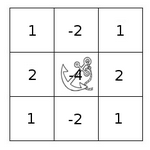
Laplacian Pyramids¶
A Laplacian pyramid is very similar to a Gaussian pyramid but saves the difference image of the blurred versions between each levels. Only the smallest level is not a difference image to enable reconstruction of the high resolution image using the difference images on higher levels. This technique can be used in image compression
Gaussian Pyramids¶
In a Gaussian pyramid, subsequent images are weighted down using a Gaussian average (Gaussian blur) and scaled down. Each pixel containing a local average that corresponds to a pixel neighborhood on a lower level of the pyramid. This technique is used especially in texture synthesis.